AI in the Healthcare Industry: Uses, Examples and Benefits

Did you know?
- Medical errors are the third biggest cause of death in the world. In the U.S. alone, they cause over 250,000 deaths every year.
- It still takes weeks or even months to diagnose serious illnesses like cancer or brain disorders.
Even with all the progress in healthcare, these facts show we have a long way to go. AI could be the missing piece. By combining fast technology with doctors’ knowledge, we can solve big problems in healthcare and save more lives.
What’s AI in Healthcare:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare basically refers to the use of AI technologies like learning from patterns (machine learning), understanding language (natural language processing), and advanced data interpretation (deep learning) to analyze complex medical data, improve diagnostics, optimize treatments, and enhance patient care.
Artificial intelligence can often match and sometimes even outperform human decision-making, especially when analyzing large amounts of data quickly by delivering faster, more accurate, and cost-effective solutions.
Although AI’s early foundations were laid in the 1950s, its real impact began in the 2000s with AI-driven disease detection and FDA-approved AI-powered devices. Today, AI supports preventive screenings, automates diagnostic imaging, aids in drug discovery, assists in robotic surgeries, and enhances personalized treatments.
AI in Healthcare Market Size;-
AI in healthcare is booming. In 2024, the market was valued at $26.69 billion. By 2025, it’s expected to grow to $36.96 billion, and by 2034, it could reach a massive $613.81 billion. That’s a yearly growth rate of 36.83% which is pretty incredible.
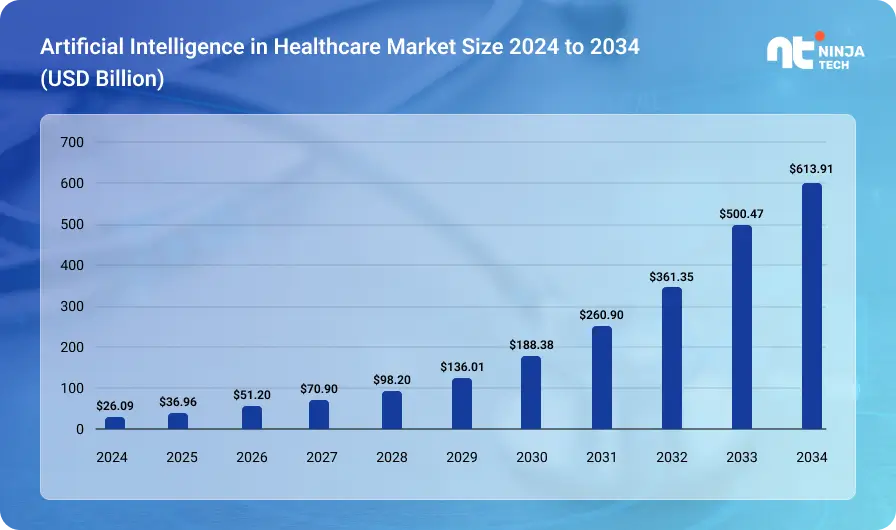
So, what does this mean? It means healthcare is changing fast. Hospitals, labs, and drug makers are turning to AI to get things done faster, more accurately, and at a lower cost.
Just like AI is helping in everyday life, it’s becoming a powerful part of the healthcare system too.
How Artificial Intelligence Works in Medical Services
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a range of advanced tools that allow machines to mimic human thinking, such as learning from data, making choices, and solving problems. In the healthcare world, AI uses smart systems to process and understand different types of information, like text, images, sound, and videos to uncover useful patterns and insights.
A key part of AI is machine learning, which allows systems to “learn” from large amounts of data without being explicitly programmed for each task.
Here are some common types of AI algorithms used in healthcare:
- Deep learning: Excellent for recognizing images and speech.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows machines to read and respond to written or spoken medical information.
- Computer vision: Allows machines to “see” and understand images, like recognizing faces or analyzing medical scans.
- Reinforcement learning: Trains systems to make decisions through trial and error over time.
These AI tools have the potential to automate, improve, and reshape many areas of healthcare. As technology continues to evolve, AI is expected to play an even bigger role in patient care, disease tracking, and medical research.
AI is becoming more capable of doing human-like tasks—but faster, cheaper, and more accurately. Just as AI is becoming part of our everyday lives, it’s also becoming deeply integrated into modern healthcare.
We’ve outlined several examples to show how this transformation is already in progress.
Role of AI in Healthcare:
Artificial Intelligence is no longer just supporting healthcare, it’s becoming a true partner. So now, let’s take a look at the role of ai in medical field;-
1] AI in Personalized Medicine
One of the most promising uses of AI in the medical field is in the area of personalized medicine. By analyzing an individual’s genetic data, lifestyle, and medical history, AI can help develop personalized treatment plans that are tailored specifically to a patient’s unique needs. This is particularly important in fields such as oncology, where genetic differences between patients can significantly affect how they respond to treatments.
Example: AI algorithms can analyze cancerous tumors’ genetic profiles to predict which chemotherapy drug will be the most effective for a specific patient, reducing unnecessary side effects and improving the likelihood of a successful treatment outcome.
2] AI in Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention
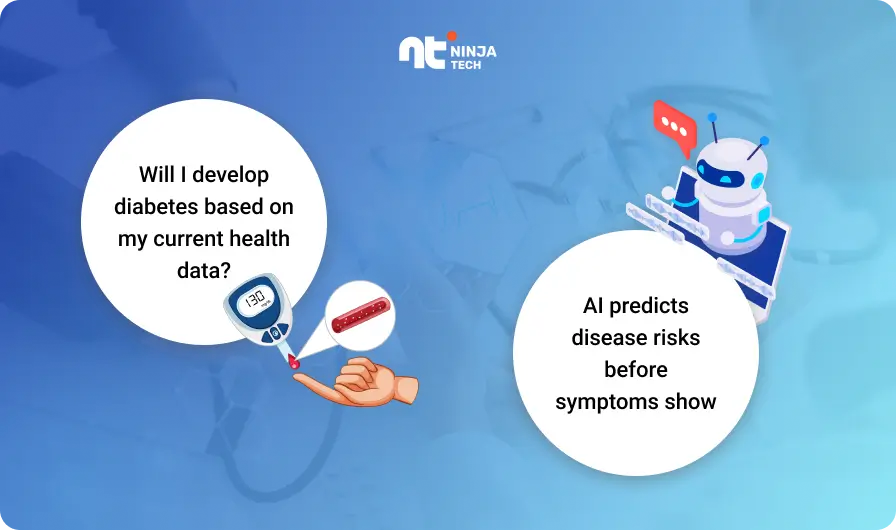
AI can be used to predict the likelihood of patients developing certain diseases based on their medical history, genetic predispositions, lifestyle, and environmental factors. This predictive capability allows healthcare providers to intervene early, preventing diseases before they become severe and reducing healthcare costs.
Example: AI models in cardiology can analyze data from wearables (such as heart rate and blood pressure) to predict heart disease risk. Based on this analysis, patients can be prescribed preventive treatments or lifestyle changes, potentially preventing heart attacks and strokes.
3] AI in Virtual Health Assistants

Virtual health assistants powered by AI can help manage patient care by offering support, answering health-related questions, providing appointment reminders, and guiding patients through post-treatment protocols. These assistants are available 24/7 and can help answer basic medical queries or direct patients to appropriate healthcare resources when necessary.
Example: Mayo Clinic uses an AI-driven virtual assistant to offer patients quick access to medical information, manage appointments, and receive follow-up care instructions. This helps in reducing patient anxiety, increases engagement, and improves the health outcomes.
4] AI in Epidemiology and Public Health

AI is also transforming the field of epidemiology by helping public health officials track and predict disease outbreaks. By analyzing patterns in population health data, AI systems can help detect the spread of diseases early, allowing for quicker interventions and more targeted response strategies.
Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI models were used to predict infection hotspots, optimize resource allocation, and forecast the impact of various public health measures, like social distancing and mask mandates. These predictive tools helped to mitigate the impact of the pandemic in many regions.
5] AI in Medical Imaging

Medical imaging is one of the areas where AI is having the greatest impact. AI algorithms can analyze medical images—such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans—faster and more accurately than human radiologists. This helps in detecting conditions like cancer, brain disorders, and heart disease at earlier, more treatable stages.
Example: Zebra Medical Vision, an AI company, uses deep learning algorithms to scan medical images and detect a wide variety of conditions, including cancers, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Their AI system has helped detect diseases earlier, leading to better treatment outcomes.
6] AI in Clinical Decision Support

AI-powered clinical decision support systems (CDSS) can assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations. These systems analyze patient data, medical literature, and clinical guidelines to suggest the most appropriate treatment plans for individual patients, helping doctors avoid errors and improve clinical outcomes.
Example: UpToDate, an evidence-based clinical decision support tool, uses AI to recommend treatment options based on the latest medical research and a patient’s specific condition. This helps doctors stay current with medical advancements while also improving patient care.
7] AI in Healthcare Fraud Detection
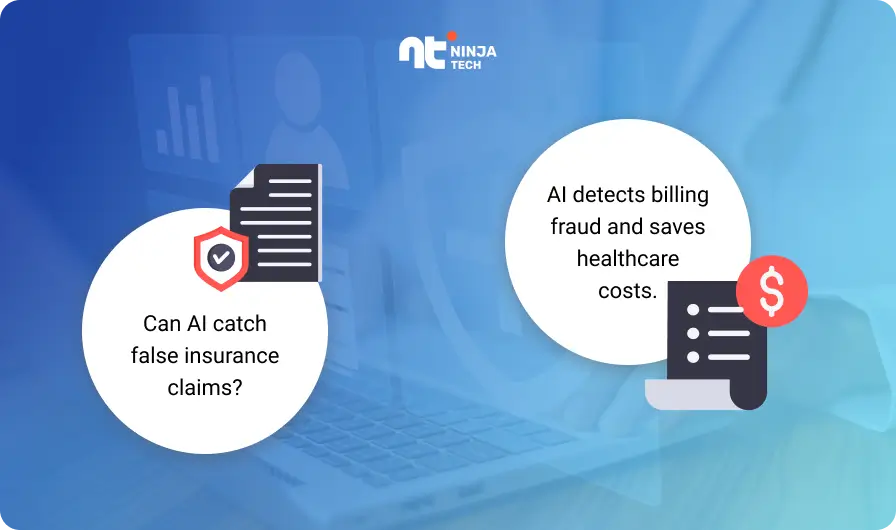
Fraudulent claims and billing errors cost the healthcare system billions of dollars annually. AI can help detect these anomalies by analyzing billing data and identifying patterns that may indicate fraudulent activity. By flagging suspicious claims in real-time, AI can help prevent fraudulent practices and reduce administrative costs.
Example: Optum, a healthcare analytics company, uses AI algorithms to analyze health insurance claims, identifying outliers or patterns that suggest fraud. Their AI-driven fraud detection system has helped save healthcare providers and insurers millions of dollars.
8] AI in Health Wearables and Monitoring Devices

Health wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are becoming increasingly common in healthcare. These devices use AI to continuously monitor a user’s vital signs, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. By tracking these metrics, AI can help detect early warning signs of health issues and recommend lifestyle adjustments to prevent them.
Example: Apple’s Health app on the Apple Watch uses AI to monitor heart rate, track daily physical activity, and even detect irregular heart rhythms. It can send alerts to users and their healthcare providers if it detects unusual patterns, such as atrial fibrillation.
9] AI in Chronic Disease Management

Managing chronic diseases like diabetes, asthma, and hypertension requires constant monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans. AI is helping to manage chronic conditions by analyzing real-time patient data from various sources, including wearable devices and patient reports, and adjusting treatment recommendations accordingly.
Example: Livongo Health, a company focused on chronic disease management, uses AI to help patients manage their diabetes. The AI-powered platform tracks patients’ blood glucose levels, activity, and diet, offering personalized coaching and alerts when intervention is necessary.
10] AI in Radiotherapy and Oncology

AI is playing a crucial role in optimizing radiotherapy for cancer patients. AI algorithms can analyze medical imaging data to plan and target radiation therapy more precisely, sparing healthy tissues while maximizing the dose delivered to the tumor. This accuracy decreases the side effects and helps to improvise treatment outcomes.
Example: Varian’s TrueBeam system uses AI to deliver radiation therapy for cancer patients. The AI-powered system adapts treatment plans in real-time, ensuring that the tumor receives maximum radiation while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
11] AI in Healthcare Recruitment
Recruiting and retaining qualified healthcare professionals is one of the most significant challenges faced by hospitals and healthcare organizations. AI can help streamline the recruitment process by screening resumes, identifying the best-fit candidates, and even conducting initial rounds of interviews through AI-powered chatbots, saving time and resources for HR departments.
Example: HireVue, an AI-powered hiring platform, assists healthcare organizations in the recruitment process by screening candidate resumes and conducting video interviews. Its AI algorithms evaluate responses based on job-specific criteria, allowing HR teams to focus on the best-qualified candidates.
12] AI in Health Risk Management
AI can predict health risks by analyzing historical patient data, genetics, and environmental factors. This predictive capability enables healthcare providers to implement early interventions and preventive measures before a patient develops serious health issues, particularly in high-risk groups like the elderly or individuals with chronic conditions.
Example: Health Catalyst uses AI algorithms to predict patients’ risk of developing conditions such as heart failure or diabetes. By analyzing data from multiple sources, including electronic health records and demographic information, the system identifies patients at high risk and recommends preventive care strategies.
13] AI in Healthcare Marketing and Patient Engagement
AI tools can be used to target patients more effectively through personalized marketing. By analyzing patient data, AI can segment patient populations and send tailored communications, such as health tips, reminders for check-ups, and promotional offers for relevant treatments. This helps healthcare organizations engage patients more effectively and increase patient loyalty.
Example: CureMetrix uses AI to optimize healthcare marketing campaigns by analyzing patient behavior and engagement patterns. The platform helps healthcare providers understand patient needs and preferences, enabling them to deliver personalized content that resonates with their audience.
14] AI in Mental Health Diagnosis and Support
Mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD are often underdiagnosed and inadequately treated. AI is improving the mental health space by helping diagnose conditions based on behavioral cues, speech patterns, and social media activity. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots and virtual therapists offer patients a level of constant, accessible care.
Example: Wysa, an AI-powered mental health chatbot, provides cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to users by engaging in text-based conversations. The AI bot uses natural language processing to offer personalized therapeutic support, making mental health care more accessible and affordable.
Advantages of AI in Healthcare
AI-powered healthcare tools bring a wide range of benefits, including:
Return on Investment:
According to a 2023 study commissioned by Microsoft and conducted by IDC, healthcare providers saw tangible returns from AI within just 14 months. On average, organizations earned $3.20 for every dollar invested in AI-related projects and initiatives.
Boost in Operational Efficiency:
Artificial intelligence helps streamline routine administrative tasks, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on direct patient care. For example, natural language processing (NLP) can automate the documentation process in electronic health records (EHRs). Generative AI tools also support customized staff training and development. Additionally, AI can manage inventory or assess operational workflows to recommend improvements.
Faster Diagnostics and Detection:
AI-integrated medical imaging systems can speed up diagnostic procedures with enhanced visual insights. These systems can identify anomalies and patterns that may go unnoticed by human reviewers. AI also supports early disease detection by analyzing genetic data and medical histories from various sources.
Expanded Access to Care and Monitoring:
AI-enabled technologies enhance access to care and monitoring, especially in remote settings. These tools can track patient vitals in real time and automate tasks during virtual consultations. In hospitals, AI platforms provide near-instant and retrospective data to optimize care delivery. Virtual nursing stations powered by AI allow a single nurse to monitor up to 50 patients from one dashboard.
Enhanced Patient Experience:
Self-service AI kiosks can streamline administrative processes like check-ins, scheduling, and payments, improving overall patient satisfaction. AI chatbots or virtual assistants can also help patients create follow-up care plans or answer non-urgent health questions by referencing provider resources.
Accelerated Research and Drug Discovery:
AI is playing an increasingly important role in life sciences research. It enhances productivity, shortens development timelines, and improves the efficiency of drug discovery and clinical trials. AI also enables personalized medicine by helping tailor treatments to individual patients.
Despite its potential, real-world adoption of AI in clinical environments remains limited. Alongside data privacy concerns, healthcare AI still faces technical and methodological hurdles that must be addressed before widespread integration.
AI in medical field: what are the major Challenges in AI Adoption
1. Bias in AI Algorithms:
AI systems often inherit biases from the datasets they are trained on. This can lead to unequal treatment recommendations, as seen in studies where Black patients received less care priority despite similar health conditions.
2. Lack of Transparency (“Black Box” Problem):
Many AI models provide results without clear explanations, making it difficult for doctors to trust and act on AI-driven insights confidently.
3. Clinical Validation Difficulties:
An AI that performs well in theory may underdeliver in real-world hospital settings, like the sepsis prediction models that failed when deployed across different institutions.
4. Regulatory Gaps:
There is no universal framework for AI approval in healthcare. Varying regional regulations create confusion, slowing down responsible adoption.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding AI in Healthcare;-
1. Data Privacy and Security Risks:
Healthcare data is a goldmine for hackers. Poor handling of sensitive patient information can lead to breaches, misuse, or loss of trust.
2. Accountability Dilemmas:
When an AI tool makes a wrong diagnosis, who bears the responsibility — the developers, the hospital, or the physician?
3. Job Displacement Anxiety:
Automation might reduce administrative burdens but also sparks fears of healthcare roles becoming obsolete, particularly in diagnostics and administrative work.
4. Risk of Dehumanizing Care:
AI should enhance, not replace, the human touch. Over-reliance on automation risks making healthcare interactions feel cold and transactional, eroding patient trust and empathy.
Real-World Examples of AI in Healthcare:
🔹 AI-Powered Cancer Detection: In 2023, clinics in Europe started using an AI system to double-check mammogram images, catching tumors that radiologists might miss. This tool acts as a second set of eyes, helping doctors detect breast cancer earlier and more reliably. Finding cancer sooner means patients can get treated faster, improving their chances of recovery.
🔹 Accelerating Drug Discovery: In 2022, Insilico Medicine announced the first AI-designed drug candidate – a potential treatment for pulmonary fibrosis that entered Phase I clinical trials. Their AI system analyzed huge chemical libraries and proposed this new molecule in a fraction of the time traditional R&D would take. It’s a promising step, as speeding up drug discovery could bring life-saving medications to patients sooner.
🔹 AI-Driven Robotic Surgery: A landmark experiment in 2022 showed an AI-guided surgical robot successfully performing a delicate laparoscopic procedure on pig tissue without human help. The robot sutured two ends of an intestine, a complex task with precision comparable to a skilled surgeon. This breakthrough hints at a future where AI assistance in operating rooms could make surgeries safer and more consistent.
🔹 Early Detection of Sepsis: Hospitals are deploying AI to catch life-threatening conditions faster. Johns Hopkins University developed an AI system that scans patient data to spot sepsis hours before doctors normally would. In real-world trials, this early warning cut sepsis deaths by roughly 20%, showing how AI can save lives through timely intervention.
Future Trends of AI in Healthcare:-
As AI continues to mature, its role in healthcare is moving beyond diagnostics and automation. Here’s a glimpse into the trends shaping the next decade of intelligent care:
🔹 Predictive AI Powers Proactive Care
AI is enabling a shift from reactive treatments to proactive, preventive healthcare. Advanced algorithms now analyze data from medical records and wearables to predict potential health issues before symptoms even appear. These AI-driven ecosystems will soon help tailor preventive strategies to individuals transforming long-term health outcomes.
🔹 Generative AI as a Clinical Copilot
Generative AI is becoming a trusted sidekick in hospitals. In Taiwan, Chi Mei Medical Center has deployed AI copilots that generate medical reports and summarize shift notes for nurses reducing administrative overload and burnout. As these tools evolve, most clinicians may soon rely on AI to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up more time for patient care.
🔹 Digital Twins for Personalized Medicine
Imagine testing a treatment plan on your digital replica before it reaches your body that’s the idea behind AI-powered digital twins. These simulations help doctors anticipate disease progression, optimize therapies, and personalize care down to the molecular level. While still in development, this trend could redefine precision medicine in the years ahead.
🔹 AI in Mental Health and Virtual Care
From 24/7 AI chatbots offering cognitive behavioral therapy to smart platforms that triage patient concerns remotely AI is making mental healthcare more accessible, private, and timely. As virtual care grows, intelligent monitoring and conversational AI will bridge care gaps for underserved or remote populations.
🔹 Explainable & Ethical AI Becomes the Standard
With AI making high-stakes decisions, transparency is critical. Future AI systems will be designed with explainability in mind — helping clinicians understand how conclusions are reached. Regulatory frameworks are also tightening, ensuring fairness, accountability, and human oversight remain at the core of AI-powered care.
Conclusion:In conclusion, AI’s growing presence in healthcare is evident in areas ranging from medical diagnostics and personalized patient care to cost management and operational efficiency. This case study highlights how these successes, while promising, are tempered by crucial ethical considerations such as privacy, fairness, and transparency.
Yet the trajectory remains overwhelmingly positive, as ongoing innovation and conscientious oversight in AI applications promise to further elevate healthcare outcomes. Ultimately, healthcare stakeholders are invited to embrace AI’s potential as a partner to human expertise. By partnering with an AI development agency, you can shape a future defined by more effective, compassionate patient care.


